SBIN
Equity Metrics
January 13, 2026
State Bank of India
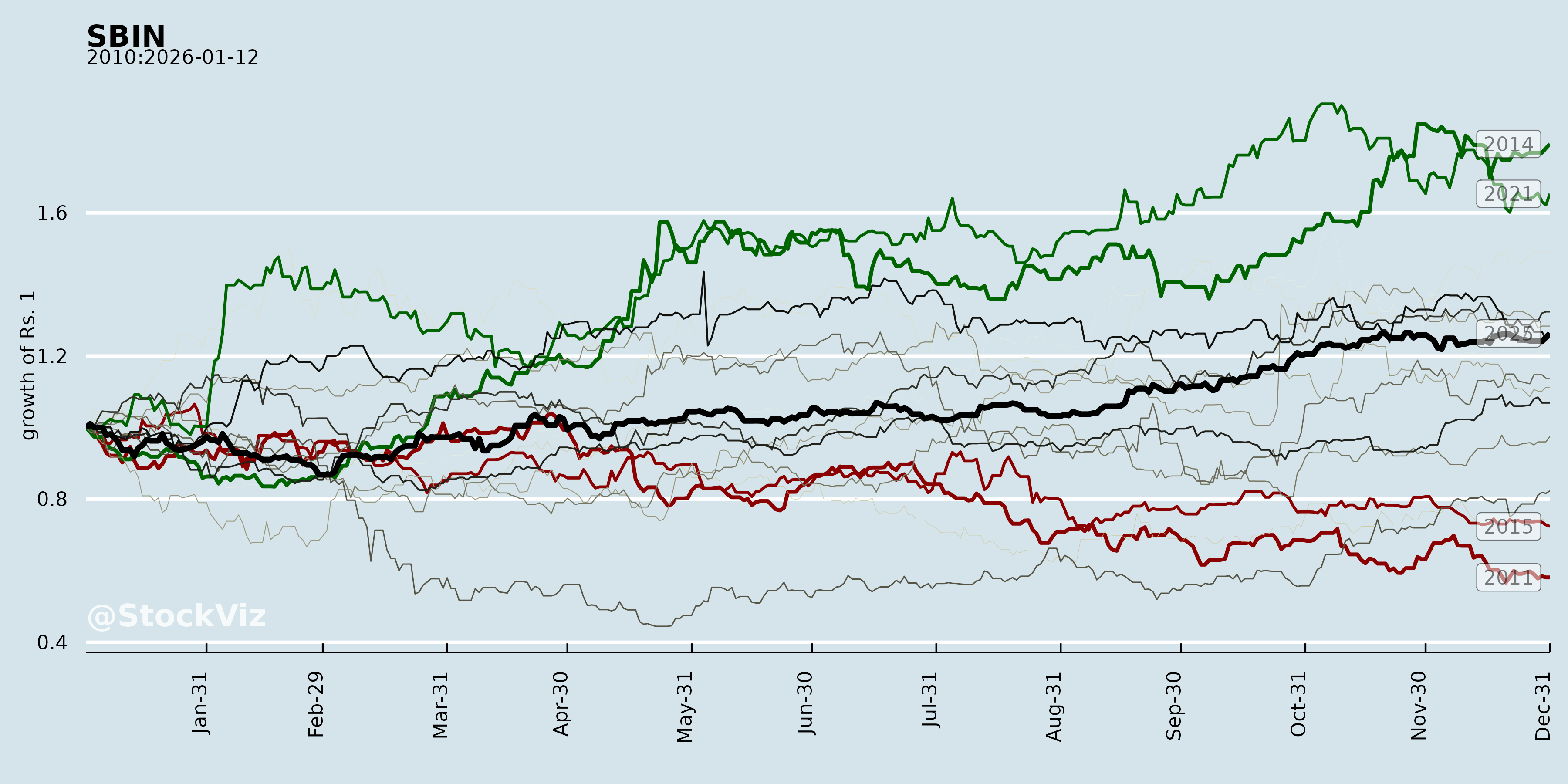
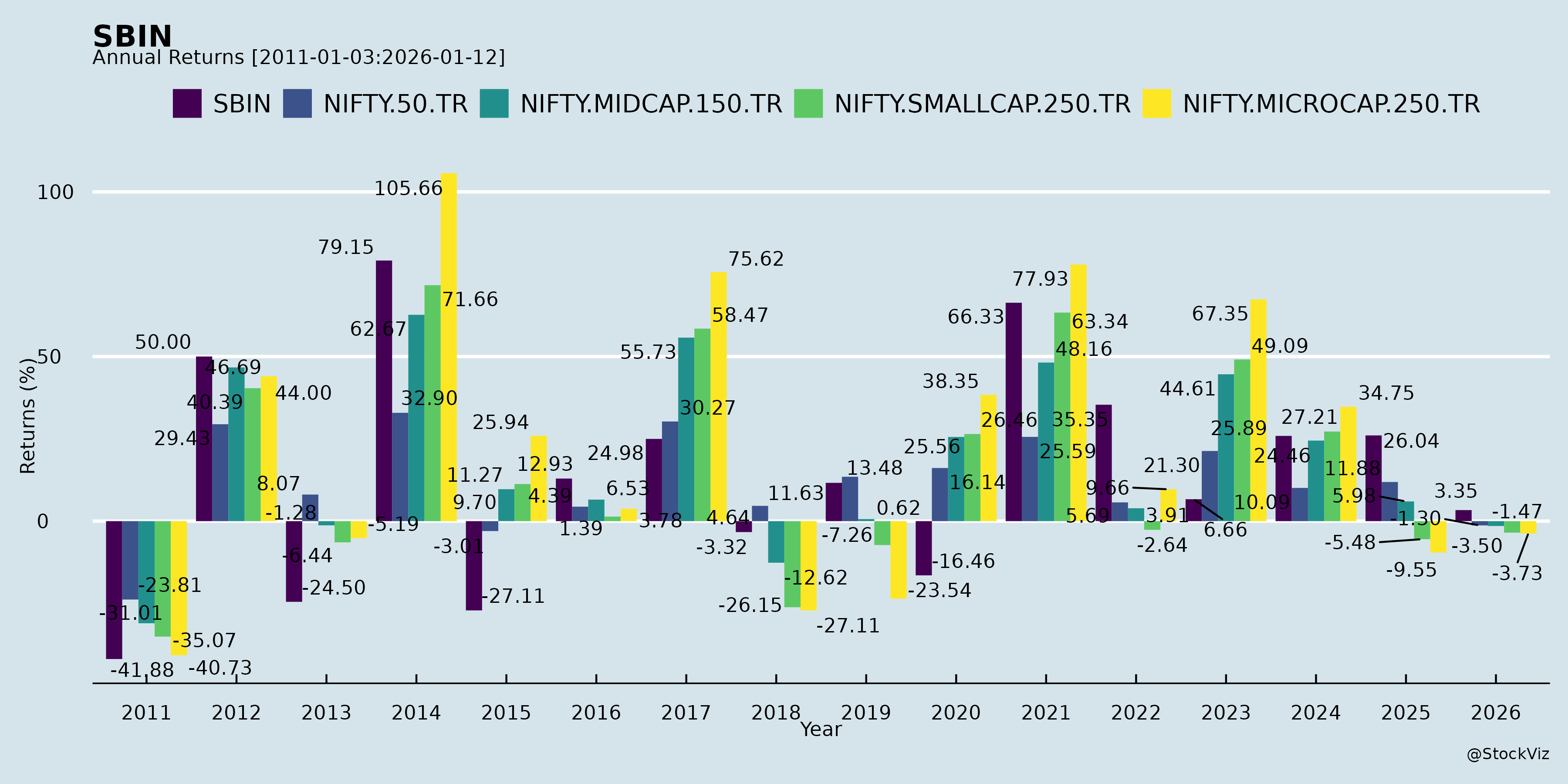
Annual Returns
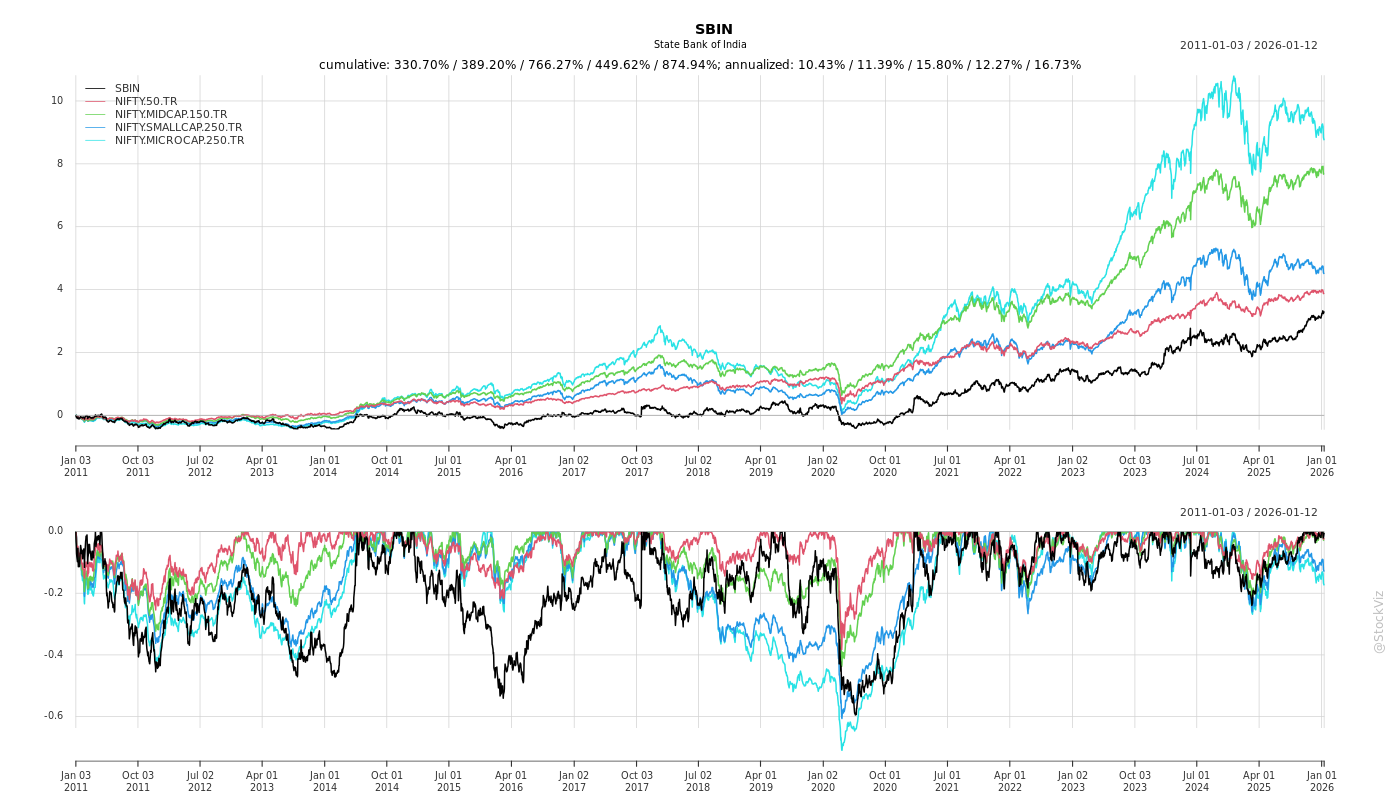
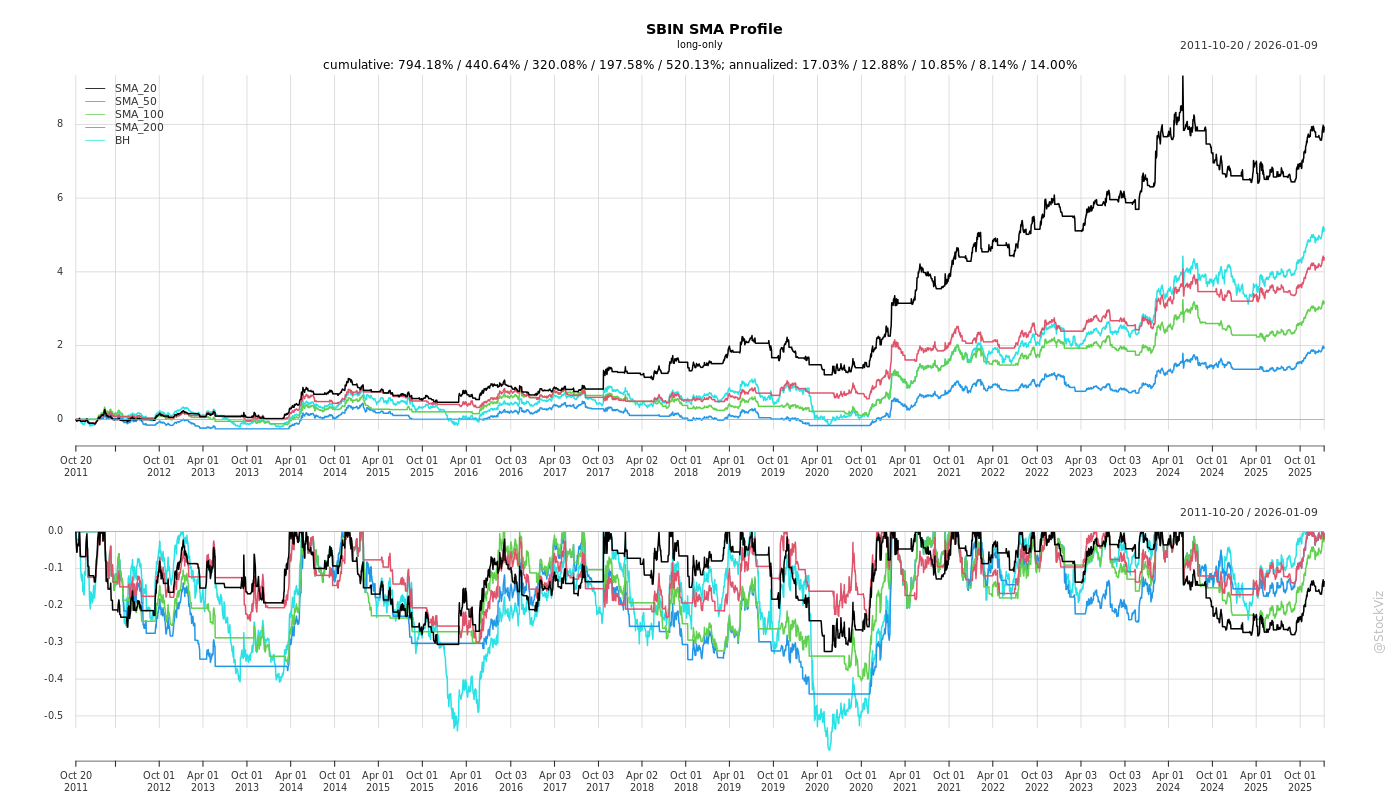
Cumulative Returns and Drawdowns
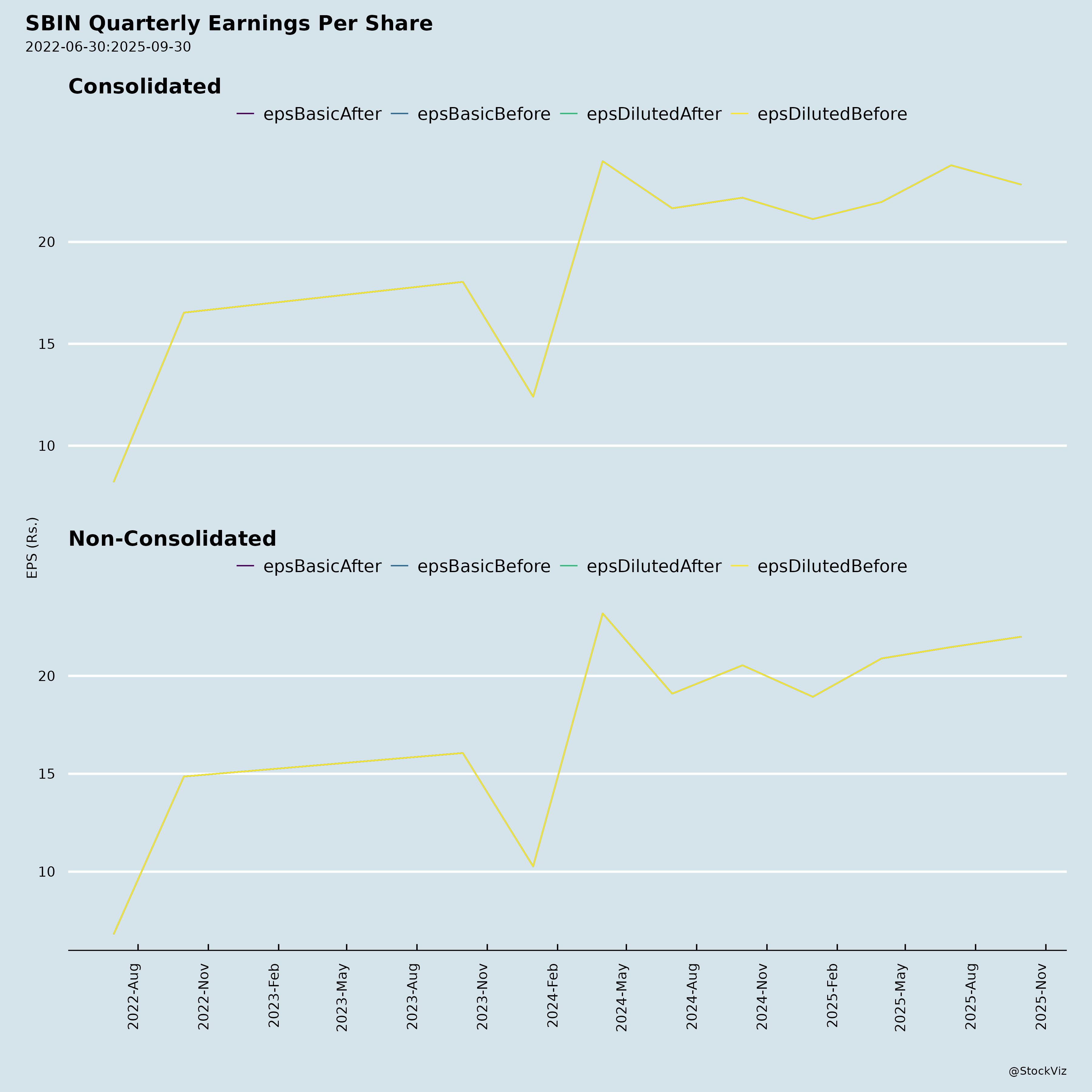
Fundamentals


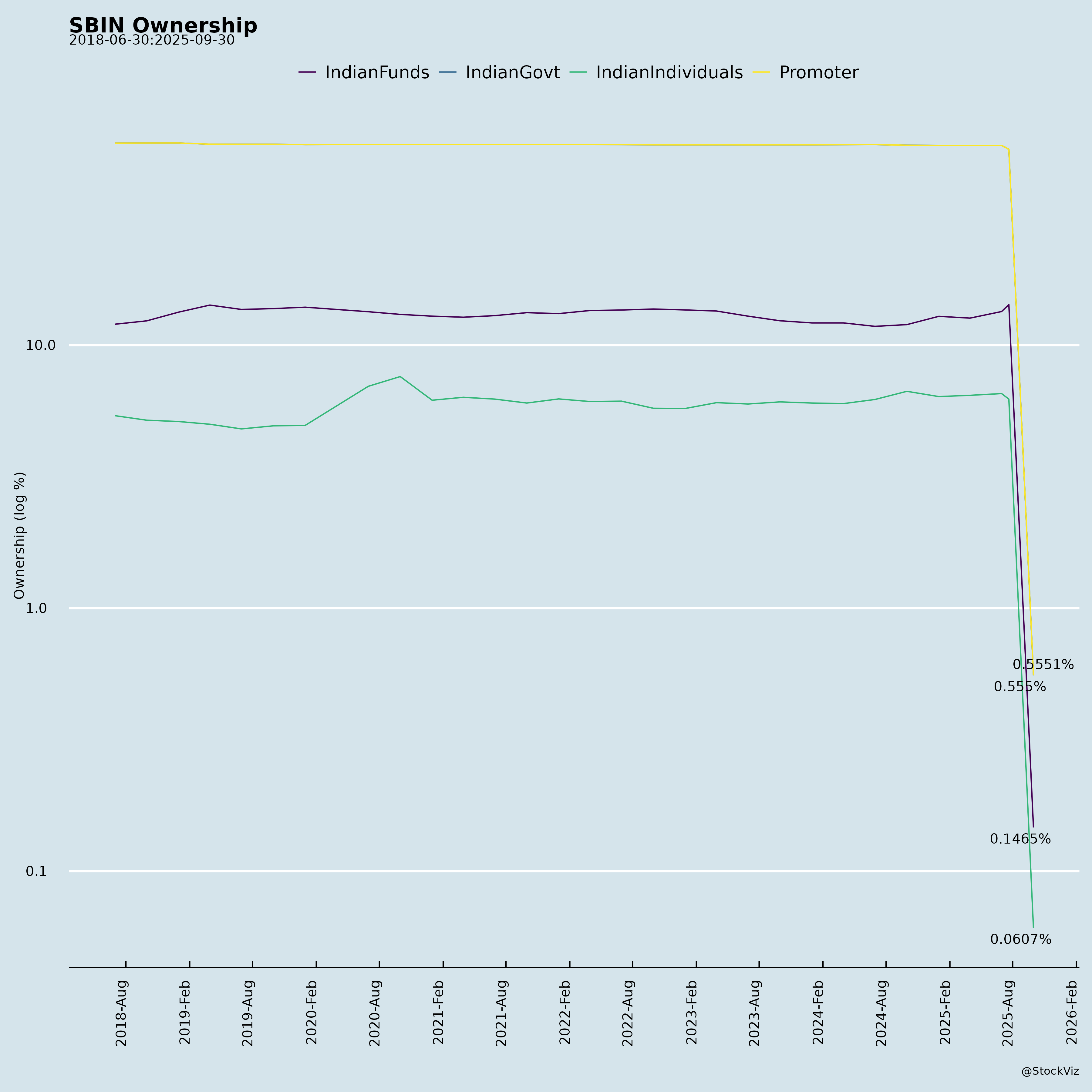
Ownership
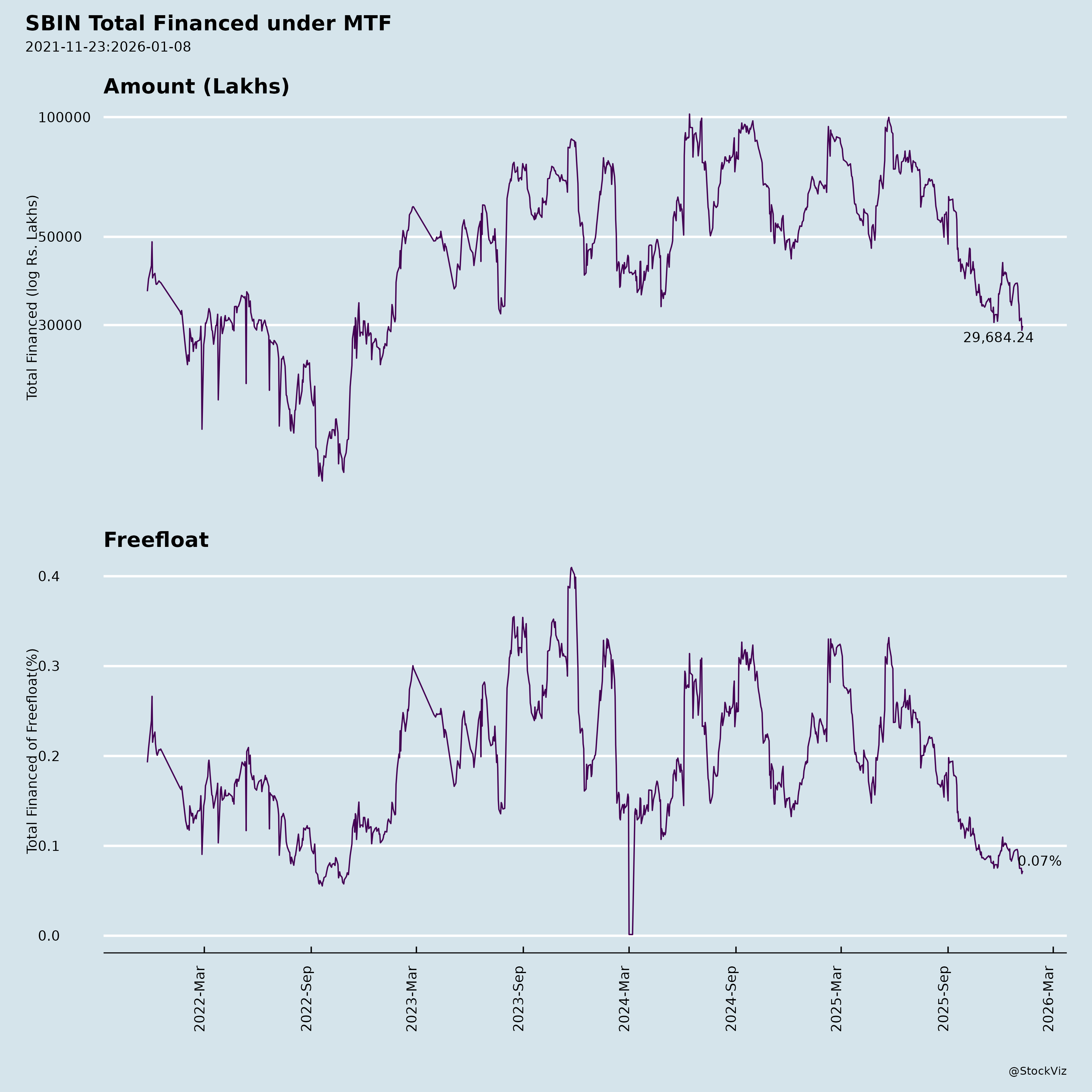
Margined
AI Summary
asof: 2025-12-08
Stock Analysis: SBI (State Bank of India) – NSE: SBIN, BSE: 500112
Based on Disclosure Regarding IPO of SBI Funds Management Limited (SBIFML)
Date of Disclosure: November 6, 2025
Summary
The recent disclosure by State Bank of India (SBI) regarding the proposed Initial Public Offering (IPO) of its subsidiary SBI Funds Management Limited (SBIFML) presents significant implications for SBI (SBIN). This move marks a strategic step toward unlocking shareholder value, enhancing transparency, and strengthening capital market engagement. While SBI remains primarily a banking entity, the IPO of SBIFML — India’s largest asset management company (AMC) — is expected to influence SBI’s valuation, investor perception, and long-term growth narrative.
Below is an analysis of headwinds, tailwinds, growth prospects, and key risks for SBI (SBIN) in light of this development.
1. Tailwinds (Positive Catalysts)
1.1. Unlocking Subsidiary Value through IPO
- Monetization Opportunity: SBI plans to divest 6.3% stake in SBIFML via IPO (3.2 crore shares), with Amundi also selling 3.7%. Total stake to be listed: ~10%, representing over 5 crore shares.
- Given SBIFML’s AUM of ₹16.32 trillion and 15.55% market share, the IPO could fetch a substantial valuation, likely in the range of $2–3 billion+, providing SBI with potential proceeds worth ₹12,000–18,000 crore (subject to final pricing).
- Historical Precedent: The listings of SBI Cards (SBICARD) and SBI Life Insurance (SBILIFE) were value-accretive. This IPO is expected to replicate or exceed those successes.
1.2. Improved Parent Company Valuation & Visibility
- The listing will enhance SBI’s investor appeal, showcasing its diversified revenue streams beyond traditional banking.
- Markets may re-rate SBI upwards due to better visibility into the high-margin asset management business, improving overall price-to-book (P/B) valuation.
- Increased transparency and governance standards post-IPO can reflect positively on the parent company.
1.3. Retention of Strategic Control
- Post-dilution, SBI will still hold ~55.6% stake in SBIFML (down from 61.91%), ensuring continued control and ongoing dividend inflows.
- Stable revenue stream from fee-based income (management fees on AUM) continues, offering predictable earnings.
1.4. Strong Fundamentals of SBIFML
- Market Leadership: SBIFML manages ₹11.99 trillion QAAUM (Q2 FY26) in mutual funds — the highest among Indian AMCs.
- Robust Distribution Network: Deep integration with SBI’s vast branch network (over 22,000 branches) gives unparalleled reach.
- Strong Growth Trajectory: As India’s mutual fund penetration rises (currently low at <5% of GDP), AUM growth potential remains high.
1.5. Positive Sentiment & Broader Investor Participation
- IPO will bring retail and institutional attention to SBIFML and, by association, SBI.
- May attract diversified investor base to SBI stock, including those favoring financial services exposure via mutual funds.
2. Headwinds (Challenges & Constraints)
2.1. Regulatory and Market Timing Risks
- IPO is subject to regulatory approvals from SEBI and other authorities. Delays possible depending on macroeconomic and market conditions (e.g., equity market volatility in 2026).
- Execution Risk: IPO could be withdrawn or downsized if capital market conditions deteriorate.
2.2. Value Recognition Lag
- Proceeds from the IPO will likely not be immediate or fully recognized in FY2026, potentially delaying positive impact on SBI’s balance sheet or capital adequacy.
- One-time gain may not be recurring, and market may discount it post-event unless future spin-offs are expected.
3. Growth Prospects
3.1. Long-Term AUM Expansion Tailwinds
- India’s mutual fund industry AUM is growing at ~15–20% CAGR. With rising financialization of savings, digital adoption, and SIP culture (over 6.6 crore SIP accounts as of 2025), SBIFML is well-positioned to grow AUM further.
- Potential to expand alternatives business (private equity, REITs, infrastructure funds) where SBIFML already manages ₹16.32 trillion.
3.2. Platform for Further Subsidiary Monetization
- SBIFML IPO could set a precedent for further divestments in SBI’s non-core subsidiaries (e.g., SBI General Insurance, SBI Capital Markets).
- Indicates SBI’s proactive capital optimization strategy, appealing to institutional investors.
3.3. Synergies with SBI’s Core Banking Business
- Cross-selling of mutual funds through SBI’s massive customer base (over 450 million customers) ensures low-cost distribution.
- Depositors can be converted to investors, deepening customer lifetime value.
4. Key Risks
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| IPO Failure or Underperformance | If market sentiment sours (e.g., due to global rate hikes, inflation in 2026), the IPO may be delayed, priced lower, or fail to attract investor interest. |
| Regulatory Scrutiny | SEBI or other regulators may impose stringent disclosure or structural requirements, delaying listing. |
| Deterioration in SBIFML Performance | A sharp correction in equity markets or poor fund performance could reduce AUM and IPO valuation. |
| Reputational Risk | Any governance lapses or product failures by SBIFML post-IPO could impact SBI’s brand. |
| Dilution of Strategic Focus | Increased focus on monetizing subsidiaries may signal shift away from core banking reform or digital initiatives. |
Conclusion & Investment Outlook
| Factor | Impact on SBIN |
|---|---|
| Short-Term (6–12 months) | Positive sentiment, potential rerating on IPO announcement. Stock may react positively to progress updates. |
| Medium-Term (1–2 years) | Proceeds from IPO could enhance capital position or support dividend payouts. Risk of “sell the news” after IPO completion. |
| Long-Term | Strengthens SBI as a financial conglomerate with high-growth, fee-based subsidiaries. Supports sustained earnings diversification. |
Overall Rating: Constructive / Positive
- Tailwinds > Headwinds: The IPO is a value-enhancing move with strong strategic rationale.
- Growth Potential: SBIFML operates in a high-conviction sector (asset management) with strong tailwinds.
- Risks are Manageable: Regulatory and market-related risks are typical for IPOs, but SBI’s brand and SBIFML’s dominance reduce execution risk.
Recommendation (for Investors)
- Hold / Accumulate: The IPO process adds optionality and visibility to SBI’s valuation. Investors should view this as a positive structural development, reinforcing SBI’s leadership beyond banking.
- Monitor IPO progress, regulatory filings, and market conditions in H1 2026 for further insights.
Disclaimer: This analysis is based solely on the provided disclosure document and does not constitute investment advice. Investors should consult a financial advisor and review official filings before making investment decisions.
Copyright © 2023 SAS Data Analytics Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.