ICICIBANK
Equity Metrics
January 13, 2026
ICICI Bank Limited
Annual Returns
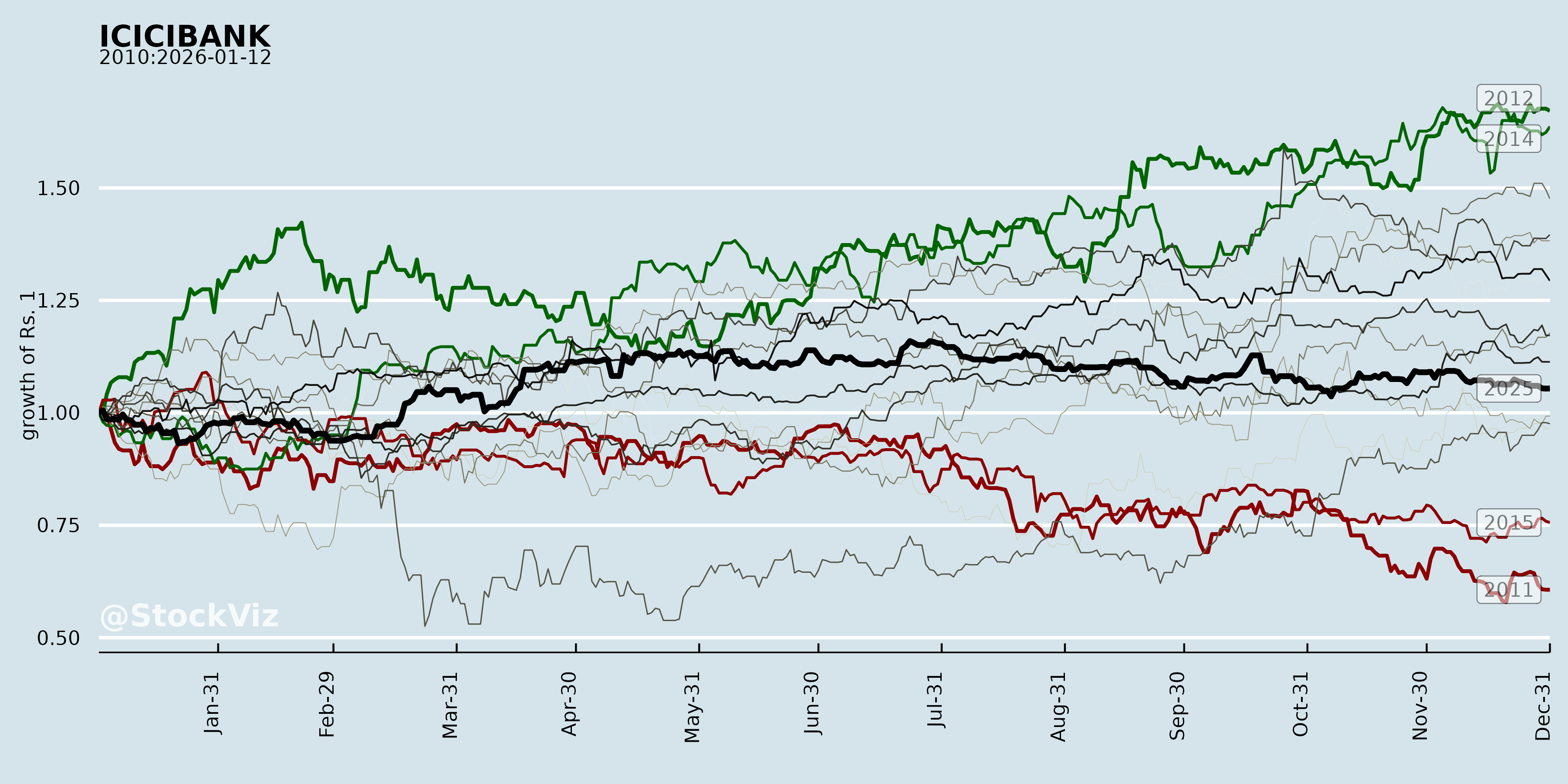
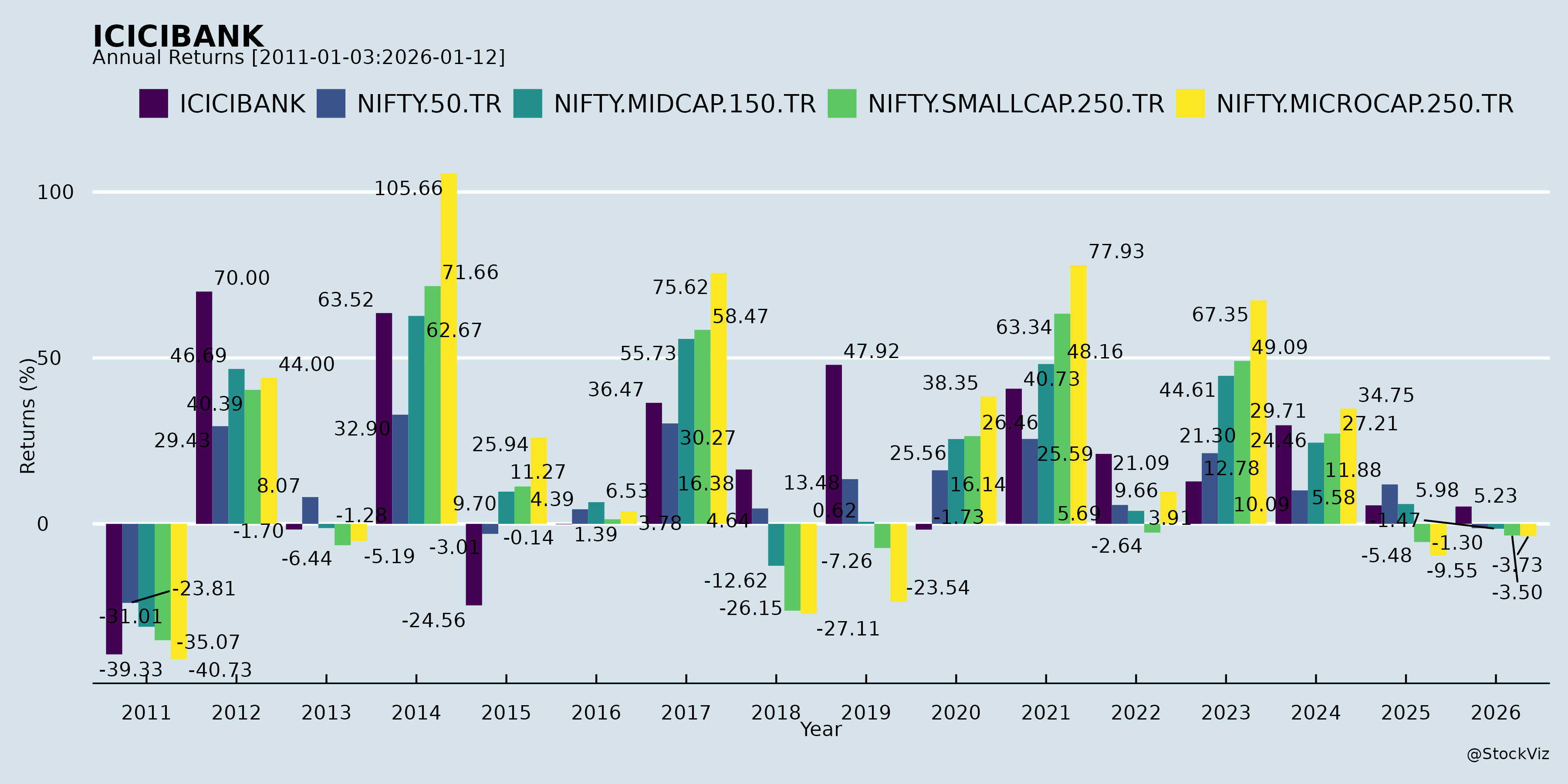
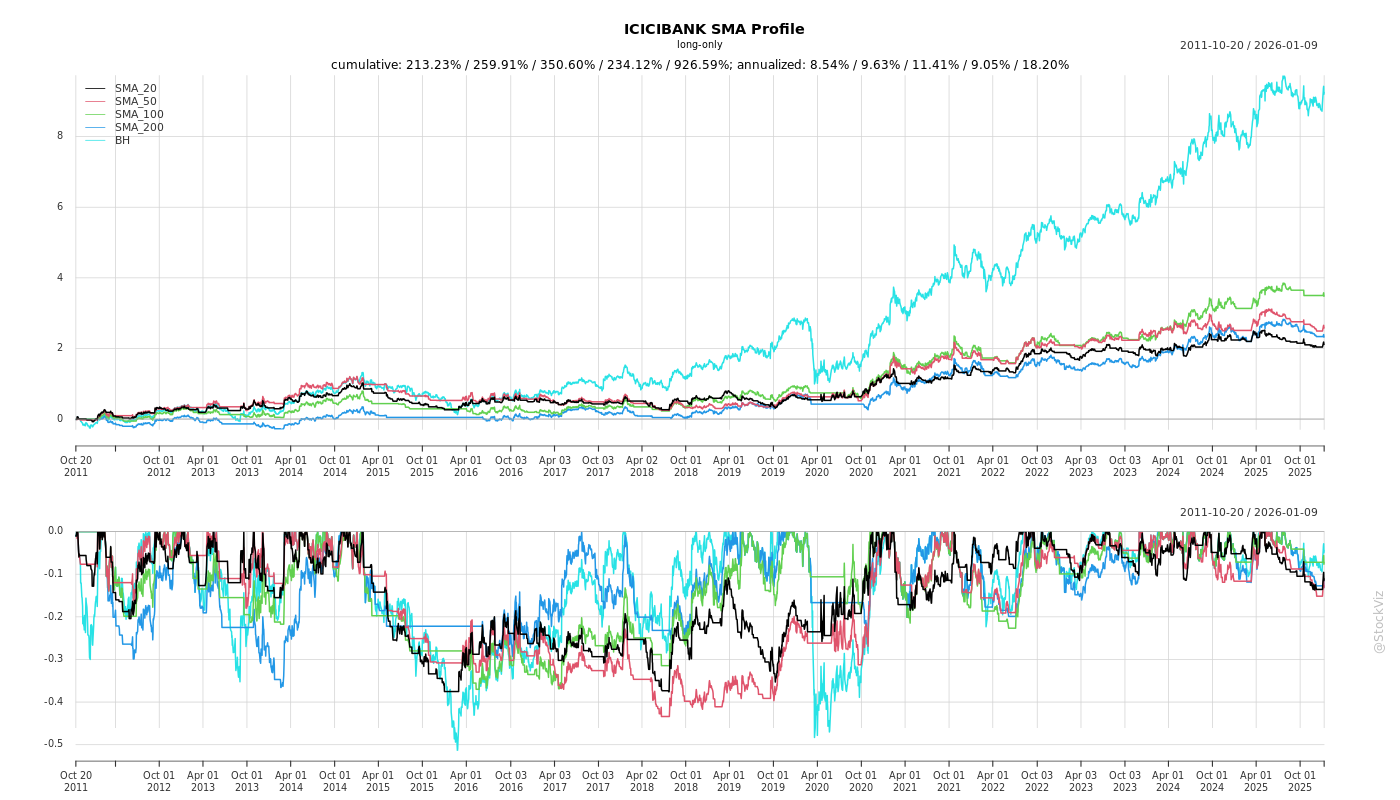
Cumulative Returns and Drawdowns

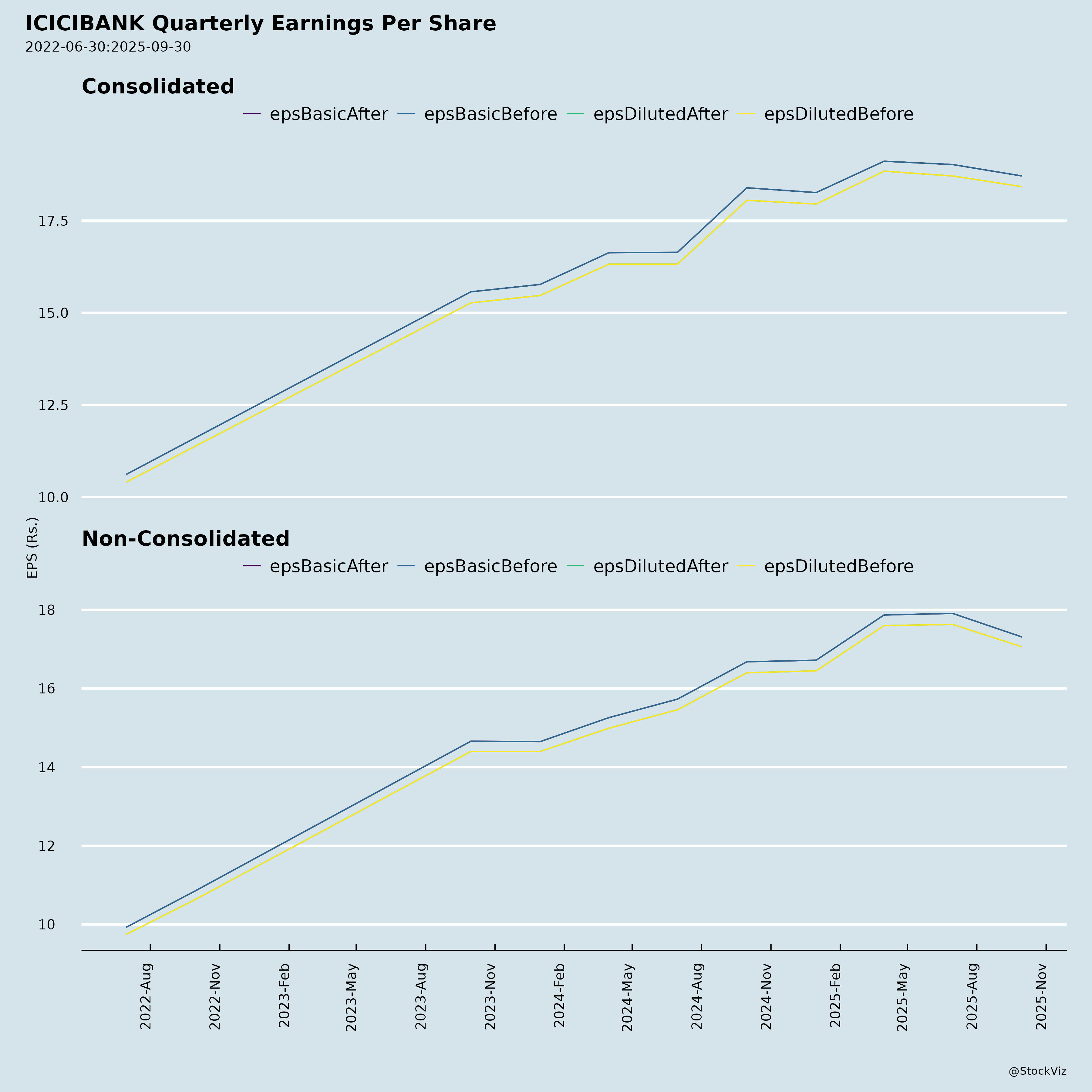
Fundamentals


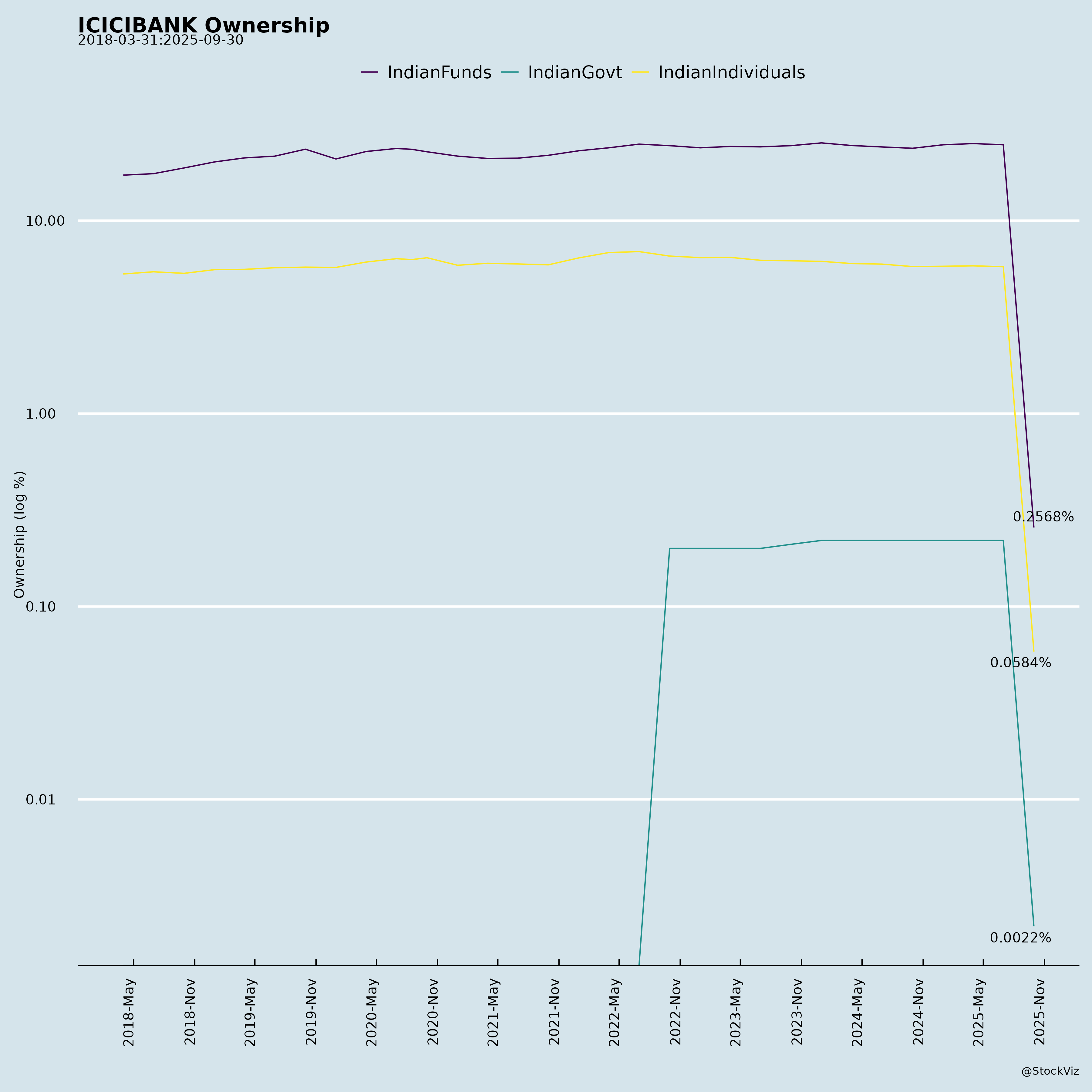
Ownership
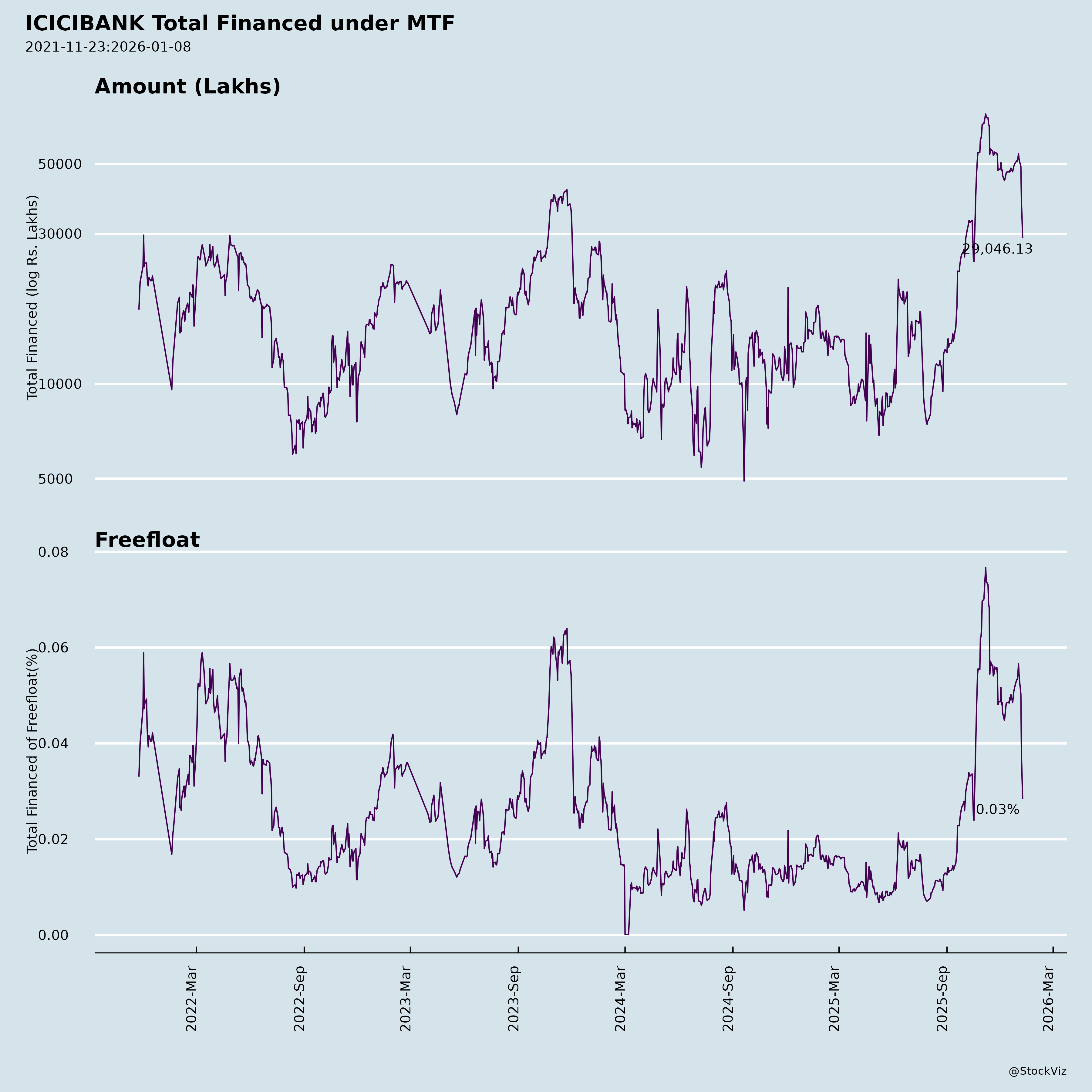
Margined
AI Summary
asof: 2025-12-08
As of the available data and documentation up to June 2024, here is a comprehensive analysis of ICICI Bank (ICICIBANK), one of India’s leading private-sector banks, focusing on the key headwinds, tailwinds, growth prospects, and risks. This assessment aggregates insights from financial reports, macroeconomic trends, regulatory developments, and industry dynamics relevant to Indian banking.
ICICI Bank: Summary Analysis
1. Tailwinds (Growth Enablers)
a) Strong Financial Performance & Consistent Profitability: - ICICI Bank has demonstrated robust earnings growth, with improved net interest margins (NIMs) and enhanced fee income. Its profitability (Return on Equity ~15–17%) remains among the highest in the Indian banking sector. - Strong loan growth (particularly in retail and SME segments) has driven top-line expansion, outpacing some peers.
b) Growing Retail and MSME Lending Franchise: - Strategic shift toward retail and MSME loans (over 50% of total book) has improved asset quality and diversification. - Retail loans — especially home, auto, and unsecured personal loans — are growing rapidly, supported by rising urban income and digital lending platforms.
c) Digital Transformation & Technology Edge: - Leading digital banking platform (ICICI Bank iMobile, digital onboarding tools) strengthens customer acquisition and reduces service overhead. - Investments in AI, data analytics, and cybersecurity position ICICI well for future scalability and cost efficiency.
d) Economic Tailwinds – India’s Macro Resilience: - India’s GDP growth remains strong (~6–7% annually), providing favorable conditions for credit growth and financial deepening. - Government’s fiscal push, infrastructure spending, and formalization of economy support corporate and consumer credit demand.
e) Deposit Franchise Strength: - Low-cost current and savings account (CASA) ratio remains high (~40–42%), giving ICICI a competitive edge in funding costs relative to peers.
2. Headwinds (Challenges)
a) Rising Competition in Retail Lending: - Intensifying competition from HDFC Bank (post-merger), SBI, and fintech NBFCs in unsecured and consumer loans could pressure margins and increase reliance on riskier assets.
b) Regulatory Scrutiny on Unsecured Lending: - The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has expressed concern over potential overheating in personal loans, particularly unsecured credit. Regulatory caps or tighter norms could slow down growth in a high-margin segment.
c) Asset Quality Pressure in Certain Segments: - While overall asset quality remains stable (GNPA ratio ~3.5%), vulnerabilities persist in: - Unsecured personal loans (small ticket, high growth). - MSME and mid-corporate exposures (sensitive to economic slowdown). - Any macroeconomic shocks (e.g., global recession, job losses, rising oil prices) could worsen delinquency trends.
d) Margin Compression Risks: - NIMs may face downward pressure due to: - High competition on loan pricing. - Rising interest rate cycles (though stable now, reversal could hurt). - Increase in higher-cost term deposits reducing CASA share.
3. Growth Prospects
a) Expansion in Rural and Semi-Urban Markets: - ICICI is expanding its branch and digital footprint in Tier 2–4 cities, capturing underpenetrated markets.
b) Wealth Management & Fee-Based Income Growth: - ICICI Securities and ICICI Prudential Life (both subsidiaries) offer significant cross-selling opportunities. - Rising financial assets, SIP inflows, and insurance penetration support future revenue diversification.
c) International Banking & NRI Focus: - Growing international operations (UK, Canada, Singapore) and focus on NRI deposits and remittances provide a stable, low-cost funding base.
d) Digital Lending & Partnerships: - Collaborations with fintechs and e-commerce platforms (e.g., BNPL, embedded finance) create scalable, low-cost distribution channels.
4. Key Risks
| Risk Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Credit Risk | Rising consumer debt levels and potential stress in unsecured personal loans. Exposures to sectors like real estate, autos, and mid-cap corporates. |
| Liquidity Risk | Dependence on term deposits; any drop in CASA could raise funding costs. |
| Regulatory Risk | RBI scrutiny on risk concentration, digital lending norms, KYC standards, and capital adequacy. |
| Cybersecurity & Operational Risk | As a digital leader, ICICI is a high-value target for cyberattacks; operational glitches could erode trust. |
| Reputational Risk | Past incidents (e.g., fraud in Russian subsidiary, internal control issues) highlight need for ongoing governance focus. |
| Macro / Geopolitical Risk | Oil price spikes, global inflation, or monetary tightening could disrupt India’s growth trajectory and credit demand. |
Summary
ICICI Bank is well-positioned as one of India’s premier financial institutions, benefiting from strong financial fundamentals, digital leadership, and a diversified retail banking model. Its robust CASA base, consistent profitability, and strategic focus on high-growth retail and MSME segments support strong growth prospects over the medium to long term.
However, challenges remain — notably increasing competition, regulatory oversight on unsecured lending, and potential macroeconomic volatility. Asset quality vigilance, prudent risk management, and continued digital innovation will be critical to sustaining performance.
Outlook: Positive, with moderate risk exposure. ICICI Bank appears well-prepared to capitalize on India’s economic growth and financial deepening, but investors should monitor lending trends, margin stability, and regulatory developments closely.
Note: This analysis is based on publicly available information as of mid-2024, including annual reports, RBI bulletins, credit ratings (CRISIL, ICRA), and Indian equity research reports. For investment decisions, current filings and market data should be referenced.
Copyright © 2023 SAS Data Analytics Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.